Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve
| Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve | |
|---|---|
|
IUCN Category III (Natural Monument)
|
|
 |
|
| Location | southern Idaho, USA |
| Nearest city | Arco |
| Area | 714,727 acres (2,892 km2) |
| Established | Monument: May 2, 1924 Preserve: August 21, 2002 |
| Visitors | 183,111 (in 2004) |
| Governing body | National Park Service and BLM |

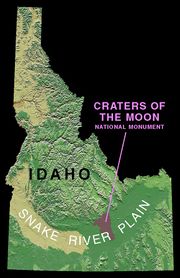
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve is a national monument and national preserve located in the Snake River Plain in central Idaho, U.S.A. It is along US 20 (concurrent with US 93 & US 26), between the small cities of Arco and Carey, at an average elevation of 5,900 feet (1,800 m) above sea level. The protected area's features are volcanic and represent one of the best preserved flood basalt areas in the continental United States.
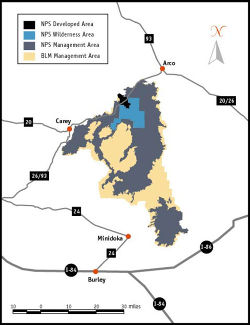
The Monument was established on May 2, 1924.[1] In November 2000, a presidential proclamation by President Clinton greatly expanded the Monument area. The National Park Service portions of the expanded Monument were designated as Craters of the Moon National Preserve in August 2002. It lies in parts of Blaine, Butte, Lincoln, Minidoka, and Power counties. The area is managed cooperatively by the National Park Service and the Bureau of Land Management (BLM).[2]
The Monument and Preserve encompass three major lava fields and about 400 square miles (1,036 km2) of sagebrush steppe grasslands to cover a total area of 1,117 square miles (2,893 km2). All three lava fields lie along the Great Rift of Idaho, with some of the best examples of open rift cracks in the world, including the deepest known on Earth at 800 feet (240 m). There are excellent examples of almost every variety of basaltic lava as well as tree molds (cavities left by lava-incinerated trees), lava tubes (a type of cave), and many other volcanic features.[3]
Contents |
Geography and geologic setting
The Craters of the Moon Lava Field spreads across 618 square miles (1,601 km2) and is the largest mostly Holocene-aged basaltic lava field in the lower 48 U.S. states.[4] The Monument and Preserve contain more than 25 volcanic cones including outstanding examples of spatter cones.[5] The 60 distinct lava flows that form the Craters of the Moon Lava Field range in age from 15,000 to just 2,000 years.[6] The Kings Bowl and Wapi lava fields, both about 2,200 years old, are part of the National Preserve.
Craters of the Moon Lava Field reaches southeastward from the Pioneer Mountains. This lava field is the largest of several large beds of lava that erupted from the 53 miles (85 km) south-east to north-west trending Great Rift volcanic zone[7]—a line of weakness in the Earth's crust created by Basin and Range rifting. Together with fields from other fissures they make up the Lava Beds of Idaho, which in turn are located within the much larger Snake River Plain volcanic province. The Great Rift almost extends across the entire Snake River Plain.
The rugged landscape remains remote and undeveloped with only one paved road across the northern end. Craters of the Moon is located in south-central Idaho midway between Boise and Yellowstone National Park, and its elevation at the visitor center is 5,900 feet (1,800 m) above sea level.[8] Combined U.S. Highway 20-26-93 cuts through the northwestern part of the monument and provides access to it.
Total average precipitation in the Craters of the Moon area is between 15–20 inches (380–510 mm) per year.[note 1][9] Most of this is lost in cracks in the basalt, only to emerge later in springs and seeps in the walls of the Snake River Canyon. Older lava fields on the plain have been invaded by drought-resistant plants such as sagebrush, while younger fields, such as Craters of the Moon, only have a seasonal and very sparse cover of vegetation. From a distance this cover disappears almost entirely, giving an impression of utter black desolation. Repeated lava flows over the last 15,000 years have raised the land surface enough to expose it to the prevailing southwesterly winds, which help to keep the area dry.[10] Together these conditions make life on the lava field difficult.
History
Native American history
Paleo-Indians visited the area about 12,000 years ago but did not leave much archaeological evidence.[11] Northern Shoshone created trails through the Craters of the Moon Lava Field during their summer migrations from the Snake River to the Camas Prairie, west of the lava field.[12] Stone windbreaks at Indian Tunnel were used to protect campsites from the dry summer wind. No evidence exists for permanent habitation by any Native American group.[12] A hunting and gathering culture, the Northern Shoshone pursued Elk, bears, American Bison, Cougars, and Bighorn Sheep—all large game who no longer range the area.[12] The most recent volcanic eruptions ended about 2,100 years ago and were likely witnessed by the Shoshone people. Shoshone legend speaks of a serpent on a mountain who, angered by lightning, coiled around and squeezed the mountain until liquid rock flowed, fire shot from cracks, and the mountain exploded.[13]
Goodale's Cutoff
European fur trappers avoided the lava field area below the Pioneer Mountains by following Indian trails. Early white pioneers who sought gold, affordable farm land to raise crops, or cheap ranch land to range cattle also avoided the lava fields and considered them useless.
Pioneers traveling in wagon trains on the Oregon Trail in the 1850s and 1860s followed an alternate route in the area that used old Indian trails that skirted the lava flows. This alternate route was later named Goodale's Cutoff and part of it is located in the northern part of the monument.[14] The cutoff was created to reduce the possibility of ambush by Shoshone warriors along the Snake River such as the one that occurred at Massacre Rocks, which today is memorialized in Idaho's Massacre Rocks State Park.
After gold was discovered in the Salmon River area of Idaho, a group of emigrants persuaded an Illinois-born trapper and trader named Tim Goodale to lead them through the cutoff. A large wagon train left in July 1862 and met up with more wagons at Craters of the Moon Lava Field.[14] Numbering 795 men and 300 women and children, the unusually large group was relatively unmolested during its journey and named the cutoff for their guide.[15] Improvements to the cutoff such as adding a ferry to cross the Snake River made it into a popular alternate route of the Oregon Trail.[15]
Exploration and early study
In 1879, two Arco cattlemen named Arthur Ferris and J.W. Powell became the first known people to explore the lava fields.[16] They were investigating its possible use for grazing and watering cattle but found the area to be unsuitable and left.
U.S. Army Captain and western explorer B.L.E. Bonneville visited the lava fields and other places in the West in the 19th century and wrote about his experiences in his diaries.[12] Washington Irving later used Bonneville's diaries to write the Adventures of Captain Bonneville, saying this unnamed lava field is a place "where nothing meets the eye but a desolate and awful waste, where no grass grows nor water runs, and where nothing is to be seen but lava."[17]
In 1901 and 1903, Israel Russell became the first geologist to study this area while surveying it for the United States Geological Survey (USGS).[11] In 1910, Samuel Paisley continued Russell's work and later became the monument's first custodian. Others followed and in time much of the mystery surrounding this and the other Lava Beds of Idaho was lifted.
The few whites who visited the area in the 19th century created local legends that it looked like the surface of the Moon. Geologists Harold T. Stearns coined the name "Craters of the Moon" in 1923 while trying to convince the National Park Service to recommend protection of the area in a national monument.[18]
Limbert's expedition
Robert Limbert, a sometime taxidermist, tanner, and furrier from Boise, explored the area, which he described as "practically unknown and unexplored ..." in the 1920s after hearing stories from fur trappers about "strange things they had seen while ranging the region".

Limbert wrote: "I had made two trips into the northern end, covering practically the same region as that traversed by a Geological Survey party in 1901. My first was a hiking and camping trip with Ad Santel (the wrestler), Dr. Dresser, and Albert Jones; the second was with Wes Watson and Era Martin (ranchers living about four miles [6 km] from the northern edge). The peculiar features seen on those trips led me to take a third across the region in the hope that even more interesting phenomena might be encountered."[19] Limbert set out on his third and most ambitious foray to the area in May 1920,[20] this time with Walter L. Cole[19] and an Airedale Terrier to accompany him.[21] Starting from Minidoka, Idaho, they explored what is now the monument area from south to north passing Two Point Butte, Echo Crater, Big Craters, North Crater Flow, and out of the lava field through the Yellowstone Park and Lincoln Highway (now known as the Old Arco-Carey Road).[15] Taking the dog along was a mistake, Limbert wrote, "for after three days' travel his feet were worn and bleeding".[21]
A series of newspaper and magazine articles written by Limbert were later published about this and previous treks, which increased public awareness of the area. The most famous of these was an article that appeared in a 1924 issue of National Geographic where he called the area "Craters of the Moon," helping to solidify the use of that name. In the article he had this to say about the cobalt blue of the Blue Dragon Flows:
- "It is the play of light at sunset across this lava that charms the spectator. It becomes a twisted, wavy sea. In the moonlight its glazed surface has a silvery sheen. With changing conditions of light and air, it varies also, even while one stands and watches. It is a place of color and silence ..."[1]
Protection and later history
In large part due to Limbert's work, Craters of the Moon National Monument was proclaimed on May 2, 1924 by U.S. President Calvin Coolidge to "preserve the unusual and weird volcanic formations".[1][21] The Craters Inn and several cabins were built in 1927 for the convenience of visitors. The Mission 66 Program initiated construction of today's road system, visitor center, shop, campground and comfort station in 1956 and in 1959 the Craters of the Moon Natural History Association was formed to assist the monument in educational activities.[22] The addition of an island of vegetation completely surrounded by lava known as Carey Kipuka (air photo) increased the size of the monument by 5,360 acres (22 km2) in 1962.[22]
Since then the monument has been enlarged. On October 23, 1970, Congress set aside a large part of it—43,243 acres (175 km2)—as Craters of the Moon National Wilderness, protecting that part under the National Wilderness Preservation System.
From 1969 to 1972, NASA visited the real Moon through the Apollo program and found that its surface does not closely resemble this part of Idaho. NASA astronauts discovered that real Moon craters were almost all created by meteorites while their namesakes on Earth were created by volcanic eruptions;[18] both are desolate. Apollo astronauts performed part of their training at Craters of the Moon Lava Field by learning to look for and collect good rock specimens in an unfamiliar and harsh environment.[23]
For many years, geologists, biologists and environmentalists have advocated for expansion of the monument and its transformation into a national park. Part of that goal was reached in 2000 when the monument was expanded 13-fold from 53,545 acres (217 km2) to its current size to encompass the entire Great Rift zone and its three lava fields.[24] The entire addition is called the Backcountry Area while the two older parts are called the Developed Area and Wilderness Area. Opposition by cattle interests and hunters to a simple expansion plan led to a compromise of having the addition become a national preserve in 2002 (which allows hunting, not ordinarily permitted in national parks and monuments in the U.S.). Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve is co-managed by the National Park Service and the Bureau of Land Management, both under the Department of the Interior.[24]
Geology

The Snake River Plain is a volcanic province that was created by a series of cataclysmic caldera-forming super-eruptions which started about 15 million years ago.[25] A migrating hotspot thought to now exist under Yellowstone Caldera in Yellowstone National Park has been implicated. This hot spot was under the Craters of the Moon area some 10 to 11 million years ago but 'moved' as the North American Plate migrated southwestward.[note 2] Pressure from the hot spot heaves the land surface up, creating fault-block mountains. After the hot spot passes the pressure is released and the land subsides.
Leftover heat from this hot spot was later liberated by Basin and Range-associated rifting and created the many overlapping lava flows that make up the Lava Beds of Idaho. The largest rift zone is the Great Rift; it is from this 'Great Rift fissure system' that Craters of the Moon, Kings Bowl, and Wapi lava fields were created.
In spite of their fresh appearance, the oldest flows in the Craters of the Moon Lava Field are 15,000 years old and the youngest erupted about 2000 years ago, according to Mel Kuntz and other USGS geologists.[7] Nevertheless the volcanic fissures at Craters of the Moon are considered to be dormant, not extinct, and are expected to erupt in less than a thousand years. There are eight major eruptive periods recognized in the Craters of the Moon Lava Field.[6] Each period lasted about 1000 years or less and were separated by relatively quiet periods that lasted between 500 to as long as 3000 years.[26]

Kings Bowl Lava Field erupted during a single fissure eruption on the southern part of the Great Rift about 2,250 years ago. This eruption probably lasted only a few hours to a few days. The field preserves explosion pits, lava lakes, squeeze-ups, basalt mounds, and an ash blanket.[5] The Wapi Lava Field probably formed from a fissure eruption at the same time as the Kings Bowl eruption. More prolonged activity over a period of months to a few years led to the formation of low shield volcanos-(?) in the Wapi field. The Bear Trap lava tube, located between the Craters of the Moon and the Wapi lava fields, is a cave system more than 15 miles (24 km) long.[24] The lava tube is remarkable for its length and for the number of well-preserved lava cave features, such as lava stalactites and curbs, the latter marking high stands of the flowing lava forever frozen on the lava tube walls. The lava tubes and pit craters of the monument are known for their unusual preservation of winter ice and snow into the hot summer months, due to shielding from the sun and the insulating properties of basalt.

A typical eruption along the Great Rift and similar basaltic rift systems starts with a curtain of very fluid lava shooting up to 1,000 feet (300 m) high along a segment of the rift up to 1 mile (1.6 km) long.[27] As the eruption continues, pressure and heat decrease and the chemistry of the lava becomes slightly more silica rich. The curtain of lava responds by breaking apart into separate vents. Various types of volcanos may form at these vents: gas-rich pulverized lava creates cinder cones (such as Inferno Cone – stop 4), and pasty lava blobs form spatter cones (such as Spatter Cones – stop 5).[7] Later stages of an eruption push lava streams out through the side or base of cinder cones, which usually ends the life of the cinder cone (North Crater, Watchmen, and Sheep Trail Butte are notable exceptions). This will sometimes breach part of the cone and carry it away as large and craggy blocks of cinder (as seen at North Crater Flow – stop 2 – and Devils Orchard – stop 3). Solid crust forms over lava streams and lava tubes (a type of cave), and are created when lava vacates its course (examples can be seen at the Cave Area – stop 7).
Geologists feared that a large earthquake that shook Borah Peak, Idaho's tallest mountain, in 1983 would restart volcanic activity at Craters of the Moon, though this proved not to be the case.[28] Geologists predict that the area will experience its next eruption some time in the next 900 years with the most likely period in the next 100 years.[note 3]
Biology
Conditions
All plants and animals that live in and around Craters of the Moon are under great environmental stress due to constant dry winds and heat-absorbing black lavas that tend to quickly sap water from living things. Summer soil temperatures often exceed 150 °F (66 °C) and plant cover is generally less than 5% on cinder cones and about 15% over the entire monument.[29] Adaptation is therefore necessary for survival in this semi-arid harsh climate.
Water is usually only found deep inside holes at the bottom of blow-out craters.[10] Animals therefore get the moisture they need directly from their food.[30] The black soil on and around cinder cones does not hold moisture for long, making it difficult for plants to establish themselves. Soil particles first develop from direct rock decomposition by lichens and typically collect in crevices in lava flows. Successively more complex plants then colonize the microhabitat created by the increasingly productive soil.
The shaded north slopes of cinder cones provide more protection from direct sunlight and prevailing southwesterly winds and have a more persistent snow cover (an important water source in early spring). These parts of cinder cones are therefore colonized by plants first.
Gaps between lava flows were sometimes cut-off from surrounding vegetation. These literal islands of habitat are called kīpukas, a Hawaiian name used for older land surrounded by younger lava. Carey Kīpuka is one such area in the southernmost part of the monument and is used as a benchmark to measure how plant cover has changed in less pristine parts of southern Idaho.[31]
Plants
There are 375 species of plant known to grow in the monument. When wildflowers are not in bloom, most of the vegetation is found in semi-hidden pockets and consists of pine trees, cedars, junipers, and sagebrush. Strategies used by plants to cope with the adverse conditions include:[32]
- Drought tolerance by physiological adaptations such as the ability to survive extreme dehydration or the ability to extract water from very dry soil. Sagebrush and Antelope Bitterbrush are examples.
- Drought avoidance by having small, hairy, or succulent leaves to minimize moisture loss or otherwise conserve water. Hairs on scorpionweed, the succulent parts of the Pricklypear Cactus, and the small leaves of the Wirelettuce are all local examples.

- Drought escape by growing in small crevices or near persistent water supplies, or by staying dormant for about 95% of the year.[9] Mosses and ferns in the area grow near constant water sources such as natural potholes and seeps from ice caves. Scabland Penstemon, Fernleaf Fleabane, and Gland Cinquefoil grow in shallow crevices. Syringa, Bush Rockspirea, Tansybush, and even Limber Pine grow in large crevices.[33] While Dwarf Monkeyflowers (photo) carry out their entire life cycle during the short wet part of the year and survive in seed form the rest of the time.
A common plant seen on the lava field is the Dwarf Buckwheat (photo), a flowering plant 4 inches (100 mm) tall with a root system 3 feet (0.91 m) wide.[9] The root system monopolizes soil moisture in its immediate area, resulting in individual plants that are evenly spaced. Consequently, many visitors have asked park rangers if the buckwheat were systematically planted.
Wildflowers bloom from early May to late September but most are gone by late August.[34] Moisture from snow-melt along with some rainfall in late spring kick-starts the germination of annual plants, including wildflowers. Most of these plants complete their entire life cycle in the few months each year that moisture levels are good. The onset of summer decreases the number of wildflowers and by autumn only the tiny yellow flowers of sagebrush and rabbitbrush remain. Some wildflowers that grow in the area are the Arrow-leaved Balsamroot, Bitterroot, Blazing Star, Desert Parsley, Dwarf Monkeyflower, Paintbrush, Scorpionweed, Scabland Penstemon and the Wild Onion.
Animals
Years of cataloging by biologists and park rangers have recorded 2000 species of insect, 8 reptiles, 169 birds, 48 mammals, and even one amphibian (the Western Toad). Birds and some rodents are seen most frequently in the Craters of the Moon area.[30] Brown Bears once roamed this area but have long ago become locally extinct. Traditional livestock grazing continues within the grass/shrublands administered by the BLM.
Most desert animals are nocturnal, or mainly active at night. Nocturnal behavior is an adaptation to both predation and hot summer daytime temperatures. Nocturnal animals at Craters of the Moon include woodrats (also called packrats), skunks, foxes, bobcats, mountain lions, bats, nighthawks, owls, and most other small desert rodents.[30]
Animals that are most active at dawn and dusk, when temperatures are cooler than mid-day, are called crepuscular. The subdued morning and evening light helps make them less visible to predators, but is bright enough to allow them to locate food. Some animals are crepuscular mainly because their prey is. Crepuscular animals in the area include mule deer, coyotes, porcupines, Mountain Cottontails, jackrabbits, and many songbirds.[30]
Some desert animals are diurnal, or primarily active during the day. These include ground squirrels, marmots, chipmunks, lizards, snakes, hawks, and eagles.[30]
Many animals have a specific temperature range where they are active, meaning the times they are active vary with the seasons. Snakes and lizards hibernate during the winter months, are diurnal during the late spring and early fall, and become crepuscular during the heat of summer. Many insects and some birds also alter their times of activity. Some animals, like ground squirrels and marmots, have one or more periods of estivation, a summer hibernation that allows them to avoid the hottest and driest periods.[30]
Several animals are unique to Craters of the Moon and the surrounding area. Subspecies of Great Basin Pocket Mouse, pika, Yellow-pine Chipmunk, and Yellow-bellied Marmot are found nowhere else.[30] Lava tube beetles and many other cave animals are found only in the lava tubes of eastern Idaho.[30]
Mule Deer
In May 1980 wildlife researcher Brad Griffith of the University of Idaho started a three year study to mark and count the Mule Deer in the monument.[35] The National Park Service was concerned that the local herd might grow so large that it would damage its habitat. Griffith found that this group of Mule Deer has developed a totally unique drought evasion strategy for its species.[35]
The deer arrive in the southern part of the pre-2000 extent of the monument mid-April each year once winter snows have melted away enough to allow for foraging. Griffith found that by late summer plants in the area have already matured and dried to the point that they can no longer provide enough moisture to sustain the deer. In late July after about 12 days above 80 °F (27 °C) and warm nights above 50 °F (10 °C) the herd migrates 5 to 10 miles (8.0 to 16 km) north to the Pioneer Mountains to obtain water from free-flowing streams and shade themselves in aspen and Douglas-fir groves.[35] Rain in late September prompts the herd to return to the monument to feed on bitterbrush until snow in November triggers them to migrate back to their winter range. This herd, therefore, has a dual summer range. It is also very productive with one of the highest fawn survival rates of any herd in the species.[36]
Afternoon winds usually die down in the evening, prompting behavioral modifications in the herd. The deer avoid the dry wind by being more active at night when the wind is not blowing.[37] In 1991 there was a three-year average of 420 Mule Deer.[37]
Recreational activities
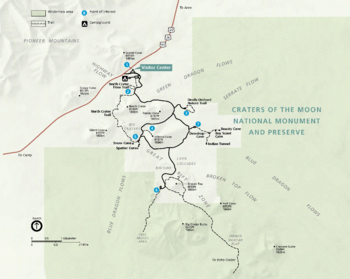
A series of fissure vents, cinder cones, spatter cones, rafted blocks, and overlapping lava flows are accessible from the Loop Drive, 7 miles (11 km) long. Wildflowers, shrubs, trees, and wild animals can be seen by hiking on one of the many trails in the monument or by just pulling over into one of the turn-offs. More rugged hiking opportunities are available in the Craters of the Moon Wilderness Area and Backcountry Area, the roadless southern and major part of the monument.
- The Visitor Center is located near the monument's only entrance. Various displays and publications along with a short film about the geology of the area help to orient visitors. Ranger-led walks are available in summer and cover topics such as wildlife, flowers, plants, or geology. Self-guiding tours and displays are available year-round and are easily accessible from the Loop Drive.
- A paved trail less than 1/4 mile (400 m) long at North Crater Flow (photo) goes through the Blue Dragon Lava Flow, which formed about 2200 years ago, making it one of the youngest lava flows on the Craters of the Moon Lava Field.[38] This lava is named for the purplish-blue tint that tiny pieces of obsidian (volcanic glass) on its surface exhibit. Good examples of pahoehoe (ropey), aa (jagged), and some block lava are readily visible along with large rafted crater wall fragments. The rafted crater wall fragments seen on the flow were once part of this cinder cone but were torn away when the volcano's lava-filled crater was breached. A 1.8-mile-long trail (2.9 km) includes the 1/2 mile (800 m) overlook trail but continues on through the crater and to the Big Craters/Spatter Cones parking lot.[38]
- Devils Orchard (photo) is a group of lava-transported cinder cone fragments (also called monoliths or cinder crags) that stand in cinders. Like the blocks at stop 2 they were once part of the North Crater cinder cone but broke off during an eruption of lava. A 1/2 mile-long (800 m) paved loop trial through the formations and trees of the "orchard" is available.[39] The interpretive displays on the trail emphasize human impacts to the area.
- Inferno Cone Viewpoint (photo) is located on top of Inferno Cone cinder cone. A short but steep trail up the cinder cone leads to an overlook of the entire monument. From there the Spatter Cones can be seen just to the south along with a large part of the Great Rift. In the distance is the over 700-foot-tall (>200 m) Big Cinder Butte, one of the world's largest, purely basaltic, cinder cones.[4] Further away are the Pioneer Mountains (behind the Visitor Center) and beyond the monument are the White Knob Mountains, the Lost River Range, and the Lemhi Range.
- Big Craters and Spatter Cones (photo) sit directly along the local part of the Great Rift fissure. Spatter cones are created by accumulations of pasty gas-poor lava as they erupt from a vent. Big Craters is a cinder cone complex located less than 300 feet (91 m) up a steep foot trail.[38]
- Tree Molds (photo) is an area within the Craters of the Moon Wilderness where lava flows overran part of a forest. The trees were incinerated but as some of them burned they released enough water to cool the lava to form a cast. Some of these casts survived the eruption and mark the exact location and shape of the burning trees in the lava. Both holes and horizontal molds were left, some still showing shapes indicative of bark. The actual Tree Molds area is located a mile (1.6 km) from the Tree Molds parking lot and picnic area off a moderately difficult wilderness trail.[38] This trail continues past the Tree Molds and 3 miles (4.8 km) further into the wilderness area before gradually disappearing near Echo Crater. A pull off on the spur road leading to the Tree Molds area presents the Lava Cascades, a frozen river of Blue Dragon Flow lava that temporarily pooled in the Big Sink.
- Cave Area is the final stop on Loop Drive and, as the name indicates, has a collection of lava tube caves. Formed from the Blue Dragon Flow, the caves are located a half-mile (800 m) from the parking lot and include,[40]
-
-
- Dewdrop Cave,
- Boy Scout Cave,
- Beauty Cave, and
- Indian Tunnel.
-
- The caves are open to visitors but flashlights are needed except in Indian Tunnel and some form of head protection is highly recommended when exploring any of the caves. Lava tubes are created when the sides and surface of a lava flow hardens. If the fluid interior flows away a cave is left behind.
Craters of the Moon Campground has 51 sites – none of which can be reserved in advance.[41] Camping facilities are basic but do include water, restrooms, charcoal grills, and trash containers. National Park Service rangers present evening programs at the campground amphitheater in the summer.

Backcountry hiking is available in the Craters of the Moon Wilderness and the much larger Backcountry Area beyond (added in 2000). Only two trails enter the wilderness area and even those stop after a few miles or kilometers. From there most hikers follow the Great Rift and explore its series of seldom-visited volcanic features. All overnight backcountry hikes require registration with a ranger. No drinking water is available in the backcountry and the dry climate quickly dehydrates hikers. Avoiding summer heat and winter cold are therefore recommended by rangers. Pets, camp fires, and all mechanized vehicles, including bicycles, are not allowed in the wilderness area.
Skiing is allowed on the Loop Drive after it is closed to traffic in late November due to snow drifts. Typically there are 20 inches (51 cm) of snow by January and 25 in (64 cm) by February.[42] Cross-country skiing off of Loop Drive is allowed but may be dangerous due to sharp lava and hidden holes under the snow. Blizzards and other inclement weather may occur.
Nearby protected areas
- Yellowstone National Park is world famous for its geysers, mudpots, Yellowstone Canyon, waterfalls, and wildlife such as the American Bison and reintroduced wolves.
- Grand Teton National Park includes the steep, glacially carved Teton Range, tectonically created Jackson Hole valley, and a string of moraine-impounded lakes.
- Nez Perce National Historical Park has 24 archaeological sites in north-central Idaho of the Nez Perce culture.[43]
- Hagerman Fossil Beds National Monument protects Pliocene-aged fossil sites along the Snake River.
- City of Rocks National Reserve contains various monoliths, spires, and domes used by the Northern Shoshone and white emigrants on the California Trail. Rock climbing is a popular activity in the reserve.
Notes
- ↑ Lower elevation areas near the Snake River average only 10–11 inches of precipitation annually.
- ↑ Meaning Craters of the Moon once looked like Yellowstone does today and Yellowstone will one day look much like Craters of the Moon does now. Actually the hot spot stays in the same place while the overlying continent of North America moves. (NPS 1991, pp. 7–12)
- ↑ Eruptions were dated using paleomagnetic and radiocarbon methods, which together give dates that are considered accurate to within 100 years (NPS 1991, pp. 28–29). Both tests were conducted in 1980 by using charred vegetation directly below individual flows (for the radiocarbon test), and from rock core samples (for the paleomagnetic work).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 NPS 1991, p. 7
- ↑ NPS website, "Management"
- ↑ Louter 1992
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Owen 2004, "Basaltic Volcanism"
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Kiver 1999, p. 340
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Kiver 1999, p. 343
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Kiver 1999, p. 339
- ↑ NPS website
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 NPS 1991, p. 35
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 NPS 1991, p. 13
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Kiver 1999, p. 338
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 NPS 1991, p. 47
- ↑ USGS website
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 NPS 1991, p. 48
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 NPS 1991, p. 49
- ↑ NPS 1991, p. 50
- ↑ Kiver 1999, p. 344
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 NPS 1991, p. 8
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 http://kencole.bravehost.com/CRATERS1.HTML
- ↑ http://www.nps.gov/archive/crmo/hcs4b.htm
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 NPS 1991, p. 51
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 NPS website, "History & Culture"
- ↑ NPS 1991, p. 9
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 Clinton 2000
- ↑ NPS 1991, p. 24
- ↑ Kiver 1999, p. 342
- ↑ NPS 1991, p. 29
- ↑ NPS 1991, p. 12
- ↑ NPS 1991, pp. 13–18
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 30.3 30.4 30.5 30.6 30.7 NPS website, "Animals"
- ↑ NPS 1991, p. 41
- ↑ NPS 1991, pp. 36–37
- ↑ NPS 1991, p. 38
- ↑ NPS 1991, p. 42
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 35.2 NPS 1991, p. 18
- ↑ NPS 1991, p. 45
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 NPS 1991, p. 19
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 38.2 38.3 NPS website, "Trail Descriptions"
- ↑ USGS website
- ↑ NPS contributors 1991
- ↑ NPS website, "Campground"
- ↑ WRCC 2007
- ↑ NPS 1991, p. 64
Bibliography
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Park Service.
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Park Service.
- Clinton, William Jefferson (November 9, 2000) (PDF). Boundary Enlargement of the Craters of the Moon National Monument. Washington, D.C.: Office of the President of the United States. Proclamation 7373. http://frwebgate.access.gpo.gov/cgi-bin/getdoc.cgi?dbname=2001_cfr_3v1&docid=3CFR7373.pdf.
- Henderson, Paul (1986). Craters of the Moon: Around the Loop. Craters of the Moon Natural History Association.
- Kiver, Eugene P.; Harris, David V. (1999). Geology of U.S. Parklands (5th ed. ed.). New York: Jonh Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-33218-6.
- Louter, David (1992). Craters of the Moon: Administrative history. Seattle, Washington: National Park Service, Pacific Northwest Region. OCLC 54665106. http://www.nps.gov/archive/crmo/adhit.htm. Retrieved 2008-08-24.
- NPS contributors (1991). Craters of the Moon: National Park Handbook (139). Washington D.C.: National Park Service Division of Publications. ISBN 0-912627-44-1.
- NPS contributors. "Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve, official website". National Park Service. pp. "Animals", "Campground", History & Culture", "Management", "Trail Descriptions". http://www.nps.gov/crmo/. Retrieved 2008-08-26. (public domain text)
- Owen, Doug (2004). "Geology of Craters of the Moon". National Park Service. http://www.nps.gov/archive/crmo/geology/geology.htm. Retrieved 2008-09-14.
- USGS contributors. "America's Volcanic Past: Craters of the Moon National Monument". United States Geological Survey. http://vulcan.wr.usgs.gov/LivingWith/VolcanicPast/Places/volcanic_past_craters_moon.html. Retrieved 2008-08-10.
- WRCC contributors (2007). "Craters of the Moon NM, Idaho (102260): Period of Record Monthly Climate Summary". Western Regional Climate Center. http://www.wrcc.dri.edu/cgi-bin/cliMAIN.pl?id2260. Retrieved 2008-09-14.
External links
- Official websites: NPS and BLM
- Presidential Proclamation 7373 (William Jefferson Clinton) – Boundary Enlargement of the Craters of the Moon National Monument (also used as a reference)
- Craters of the Moon: Historic Context Statements, National Park Service
- Geology of Craters of the Moon, National Park Service (also used as a reference)
- MSRmaps.com - USGS topo map & aerial photo
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||